What is machine learning?
Machine learning is the scientific study of algorithms and statistical models that computer systems use to affectively perform a specific task without using explicit instruction, relyring on patterns and inference instead.
Building a model by learning the patterns of historical data with some relationship between data to make a data-driven prediction.
Read more: What is the difference between supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning?
# Training Data
The relationship between the data and the machine learning model, is as critical as the fuel to the engine of rocket.
It is not exaggerating to say that the data dictates how the machine learning model is built.
# garbage in, garbage out
Group of blind men, who have never come across an elephant before, would like to learn and conceptualize what an elephant is like by touching it.
Each man touches a part of the body, such as leg, tusk or tail etc. While each of them got a part of the reality, none of them has the whole picture of an elephant. Therefore, none of them actually learned the true image of an elephant.
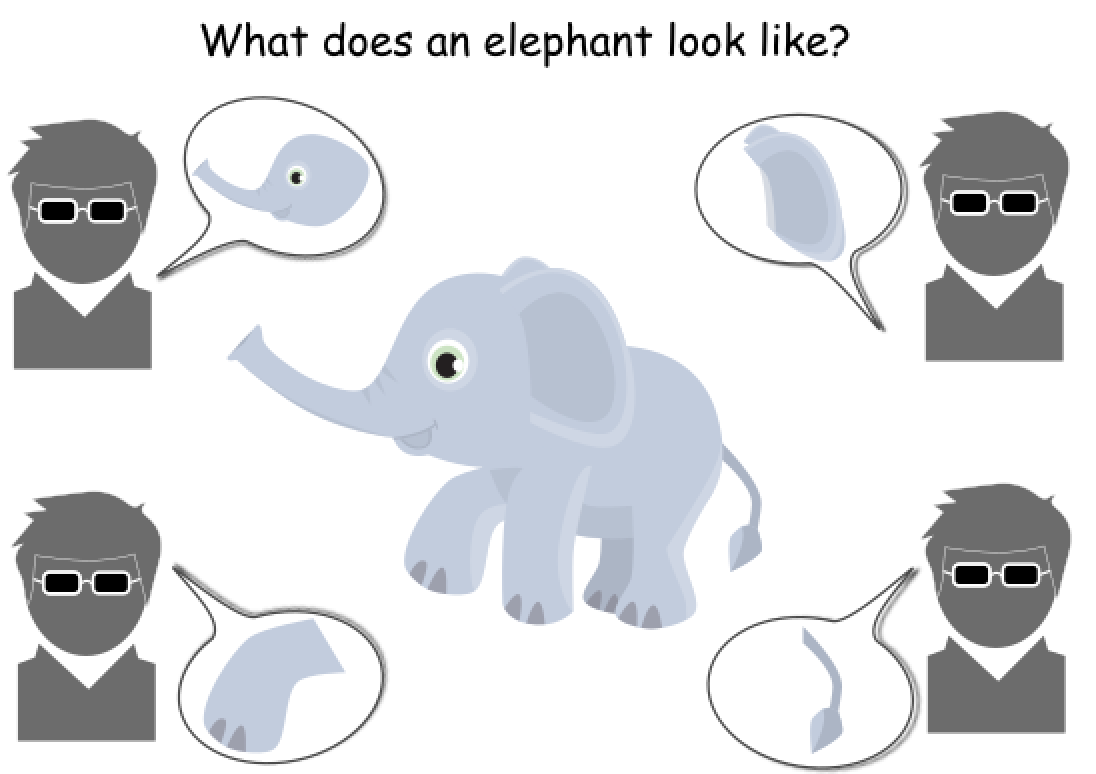
The training data we got could be those images of legs or tusks from an elephant, while during the test processing, the testing data we got are the full portraits of elephants.
It would not be surprising to find out that our trained model does not perform well in this case, since we do not have the high-quality training data that is closer to the reality in the first place.
If the data is really important, then why not feeding the “high-quality” data such as full portraits of elephants into the algorithm, instead of snapshots on parts of the elephant body?
- Because, facing a problem, we or the machine, like the “blind-men”, often struggle to gather the data that captures the essential characteristics of the problem, either due to the technical issues (e.g. data privacy) or simply because we do not perceive the problem in the right way.
# Real world data
In the real world, the data we got reflects a part of reality in a favorable case, or it could be some noise in a less favorable case, or in the worst case, even a contradiction to the reality.
Regardless of the machine learning algorithms, one would not be able to learn anything from data that contains too much noise or is too inconsistent with the reality.
# Workflow
The relationship between the data and the machine learning model, is as critical as the fuel to the engine of rocket.
# Data-Centric Workflow
